All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Which Double Glazed Windows Are Best For Summer? in Koondoola Perth
Glazing merely suggests the windows in your house, including both openable and set windows, along with doors with glass and skylights. Glazing actually just suggests the glass part, however it is generally utilized to refer to all elements of an assembly consisting of glass, films, frames and furnishings. Focusing on all of these aspects will assist you to achieve efficient passive style.

Energy-efficient glazing makes your home more comfy and significantly reduces your energy expenses. Improper or improperly developed glazing can be a major source of unwanted heat gain in summertime and considerable heat loss and condensation in winter season. Up to 87% of a home's heating energy can be gotten and up to 40% lost through windows.
Double Glazed Windows And Doors In Perth in Belmont Perth
Glazing is a substantial financial investment in the quality of your house. A preliminary investment in energy-efficient windows, skylights and doors can greatly decrease your yearly heating and cooling costs.
This tool compares window selections to a base level aluminium window with 3mm clear glass. Comprehending a few of the crucial homes of glass will assist you to choose the very best glazing for your house. Key residential or commercial properties of glass Source: Adjusted from the Australian Window Association The amount of light that travels through the glazing is referred to as noticeable light transmittance (VLT) or noticeable transmittance (VT).
What Is The Best Glazing For My Home? - Part 2 in Connolly Perth
This might lead you to turn on lights, which will lead to greater energy costs. Conduction is how readily a material performs heat. This is called the U worth. The U value for windows (revealed as Uw), explains the conduction of the whole window (glass and frame together). The lower the U worth, the higher a window's resistance to heat circulation and the much better its insulating value.
For example, if your home has 70m2 of glazing with aluminium frames and clear glass with a U worth of 6. 2W/m2 C, on a winter's night when it is 15C chillier outside compared to inside your home, the heat loss through the windows would be: 6. 2 15 70 = 6510W That is comparable to the total heat output of a large space gas heating unit or a 6.
Does Double Glazing Have A Vacuum? in Swan View WA

If you select a window with half the U value (3. 1W/m2 C) (for example, double glazing with an argon-filled space and less-conductive frames), you can halve the heat loss: 3. 1 15 70 = 3255W The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) for windows (revealed as SHGCw) determines how easily heat from direct sunshine flows through a whole window (glass and frame together).
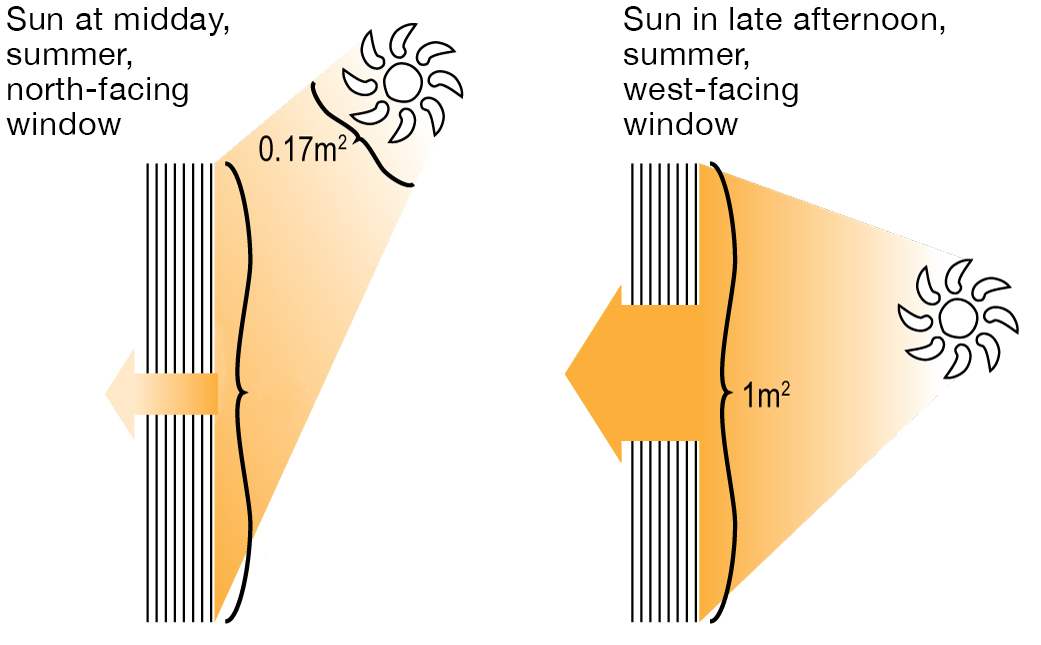
The lower a window's SHGC, the less solar heat it transfers to the home interior. Glazing producers state an SHGC for each window type and design. The actual SHGC for windows is affected by the angle that solar radiation strikes the glass. This is referred to as the angle of occurrence.
Double Glazed Windows: A Complete Guide in Hillarys Western Australia
When the sun is perpendicular (at 90) to the glass, it has an angle of occurrence of 0 and the window will experience the optimum possible solar heat gain. The SHGC stated by glazing makers is always computed as having a 0 angle of incidence. As the angle increases, more solar radiation is shown, and less is transferred.
Latest Posts
Double Glazed Windows: A Complete Guide in Sorrento Western Australia
Faq in Wellard Western Australia
Will Triple Glazing Make My House Warmer? in Darling Downs Perth